Residential Wiring Diagram Examples are crucial tools for understanding and visualizing the electrical layout of a home. Whether you are a homeowner looking to make upgrades or a professional electrician working on a project, these diagrams provide a clear and detailed representation of the electrical connections within a residence.
Why Residential Wiring Diagram Examples are Essential
Residential Wiring Diagram Examples are essential for several reasons, including:
- Understanding the overall electrical system of a home
- Identifying specific circuits and components
- Planning and executing electrical upgrades or renovations
- Troubleshooting electrical issues
How to Read and Interpret Residential Wiring Diagram Examples
Reading and interpreting Residential Wiring Diagram Examples may seem daunting at first, but with some guidance, it can become a valuable skill. Here are some tips to help you navigate these diagrams effectively:
- Start by familiarizing yourself with the symbols and abbreviations used in the diagram
- Follow the flow of electricity from the power source to the various outlets and appliances
- Pay attention to the color-coding of wires and their corresponding functions
- Refer to the legend or key provided on the diagram for additional information
Using Residential Wiring Diagram Examples for Troubleshooting
Residential Wiring Diagram Examples are invaluable when it comes to troubleshooting electrical problems in a home. By referring to the diagram, you can:
- Identify the location of specific circuits and components
- Trace the flow of electricity to pinpoint the source of the issue
- Check for any loose connections, damaged wires, or faulty components
- Implement the necessary repairs or replacements based on the information provided
Importance of Safety
When working with electrical systems and using wiring diagrams, safety should always be the top priority. Here are some safety tips and best practices to keep in mind:
- Always turn off the power supply before working on any electrical components
- Use insulated tools to avoid electrical shocks
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and goggles
- Follow local building codes and regulations to ensure compliance and safety
Residential Wiring Diagram Examples
Basic House Wiring | Non-Stop Engineering

House Electrical Wiring 101

House Wiring 101 Diagram
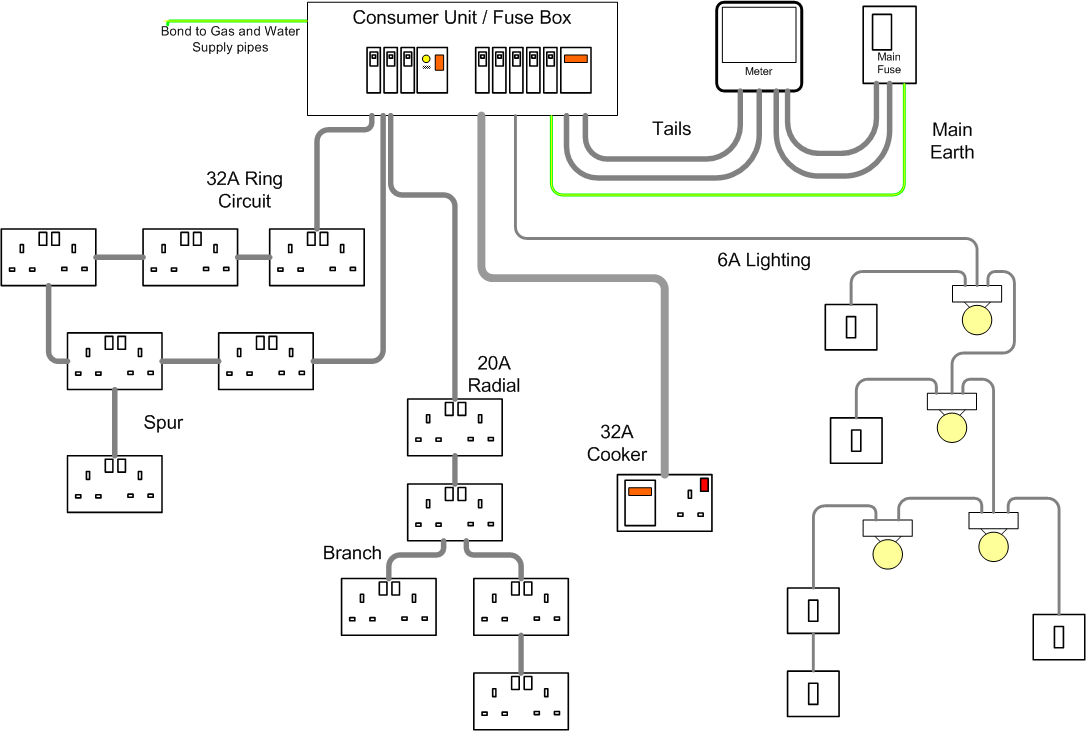
Residential House Wiring Circuit Diagram – Wiring Diagram and Schematic
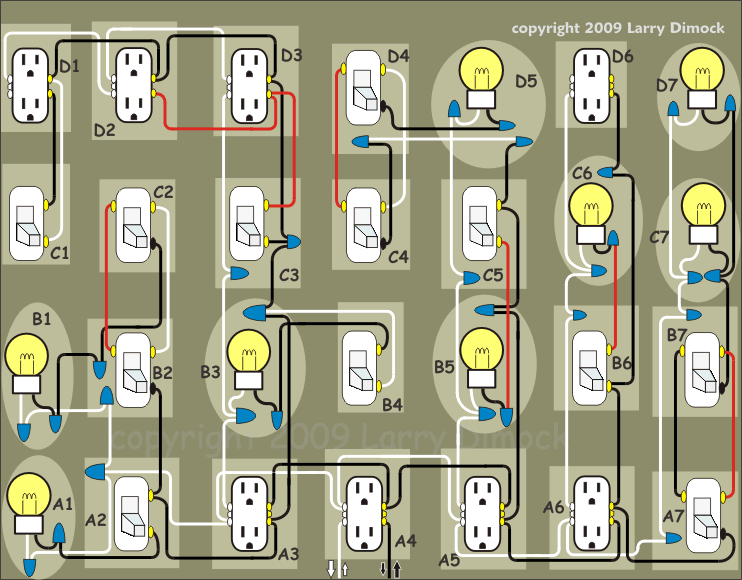
Home Electrical Wiring Basics Diagram

Simple House Wiring Diagram Examples For Your Needs
