House Wiring Diagram Examples are essential tools for understanding and visualizing the electrical layout of a house. They provide a detailed illustration of how the electrical system is structured, including the location of outlets, switches, lights, and appliances. By studying these diagrams, homeowners, electricians, and DIY enthusiasts can gain a better understanding of how electricity flows through their home.
Why House Wiring Diagram Examples are Essential
House Wiring Diagram Examples are essential for several reasons:
- Helps in planning electrical installations
- Aids in troubleshooting electrical issues
- Ensures compliance with electrical codes and regulations
- Provides a visual reference for understanding the electrical system
How to Read and Interpret House Wiring Diagram Examples
Reading and interpreting House Wiring Diagram Examples may seem daunting at first, but with a little guidance, it becomes much easier. Here are some tips:
- Start by familiarizing yourself with the symbols used in the diagram
- Follow the flow of electricity from the main panel to different outlets and fixtures
- Pay attention to the labeling and numbering of wires and components
- Refer to the legend or key provided with the diagram for clarification
Using House Wiring Diagram Examples for Troubleshooting
House Wiring Diagram Examples can be invaluable when troubleshooting electrical problems in your home. Here’s how you can use them effectively:
- Identify the specific area or circuit where the issue is occurring
- Trace the path of electricity to locate any faulty connections or components
- Compare the diagram with the actual wiring to spot any discrepancies
- Consult an electrician if you are unsure about how to proceed
Safety Tips for Working with Electrical Systems
When working with electrical systems and using wiring diagrams, safety should always be a top priority. Here are some safety tips and best practices to keep in mind:
- Always turn off the power before starting any electrical work
- Use insulated tools to prevent electrical shocks
- Avoid working in wet or damp conditions
- Wear personal protective equipment, such as gloves and safety goggles
- If in doubt, seek professional help from a qualified electrician
House Wiring Diagram Examples
Basic House Wiring | Non-Stop Engineering

House Electrical Wiring 101

How To Make A Wiring Diagram Of Your House – Floyd Wired

House Wiring for Beginners – DIYWiki
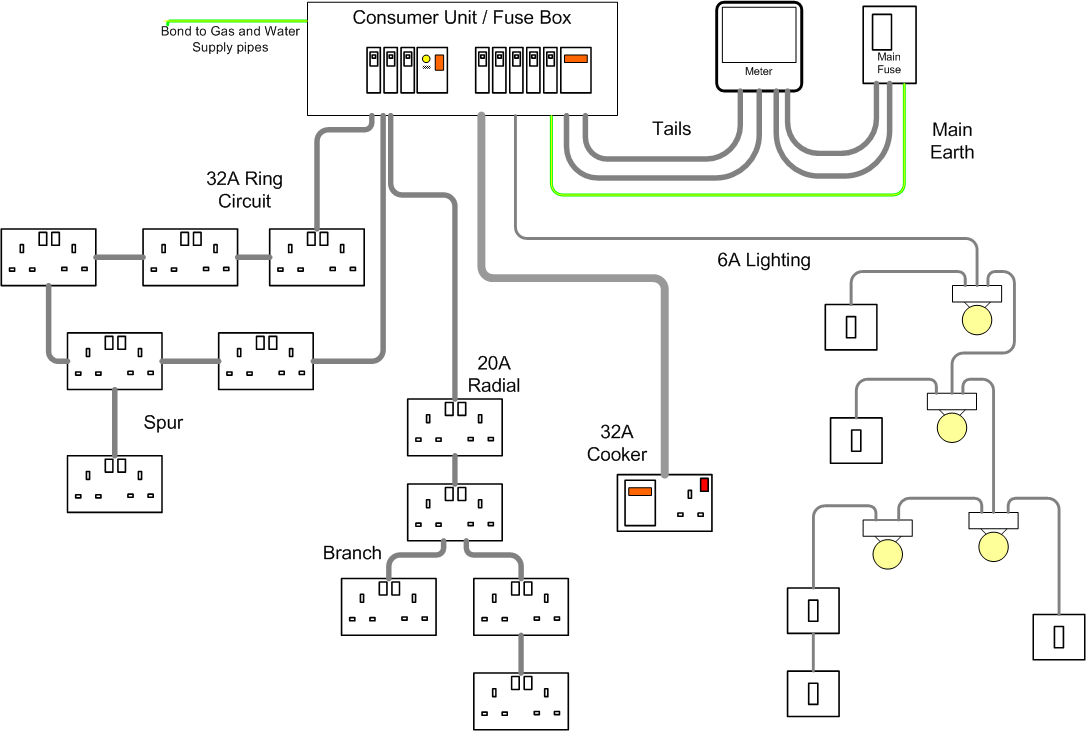
Basic Electrical Wiring Diagram House – Wiring Digital and Schematic

Complete Electrical Single Phase | House Wiring Diagram – YouTube
